Like most organizations, we're always striving to find a competitive advantage that propels us in front of our competitors. But, even when you create a competitive edge, oversaturated markets and technological advancements mean it's never long before competitors are able to replicate your competitive advantage.
A sustained competitive advantage is the holy grail, and the VRIO framework might just be our map. One of many strategic frameworks, the VRIO framework is a tool for identifying the competitive advantages of an organization (if they have any).
⚠️ Don't just identify strengths, leverage them! Understanding your competitive advantage is crucial, but true power comes from using those strengths. Cascade Strategy Execution Platform bridges the gap between VRIO analysis and strategic action. Talk to a strategy expert and translate VRIO insights into a winning, executable strategy.
In this article, we explain
- What Does The VRIO Framework Stand For?
- What Is A VRIO Analysis?
- The VRIO Framework Explained
- VRIO Analysis Pros & Cons
- VRIO Analysis Example
- VRIO Resources
- VRIO Analysis For A Sustainable Competitive Advantage
What Does The VRIO Framework Stand For?
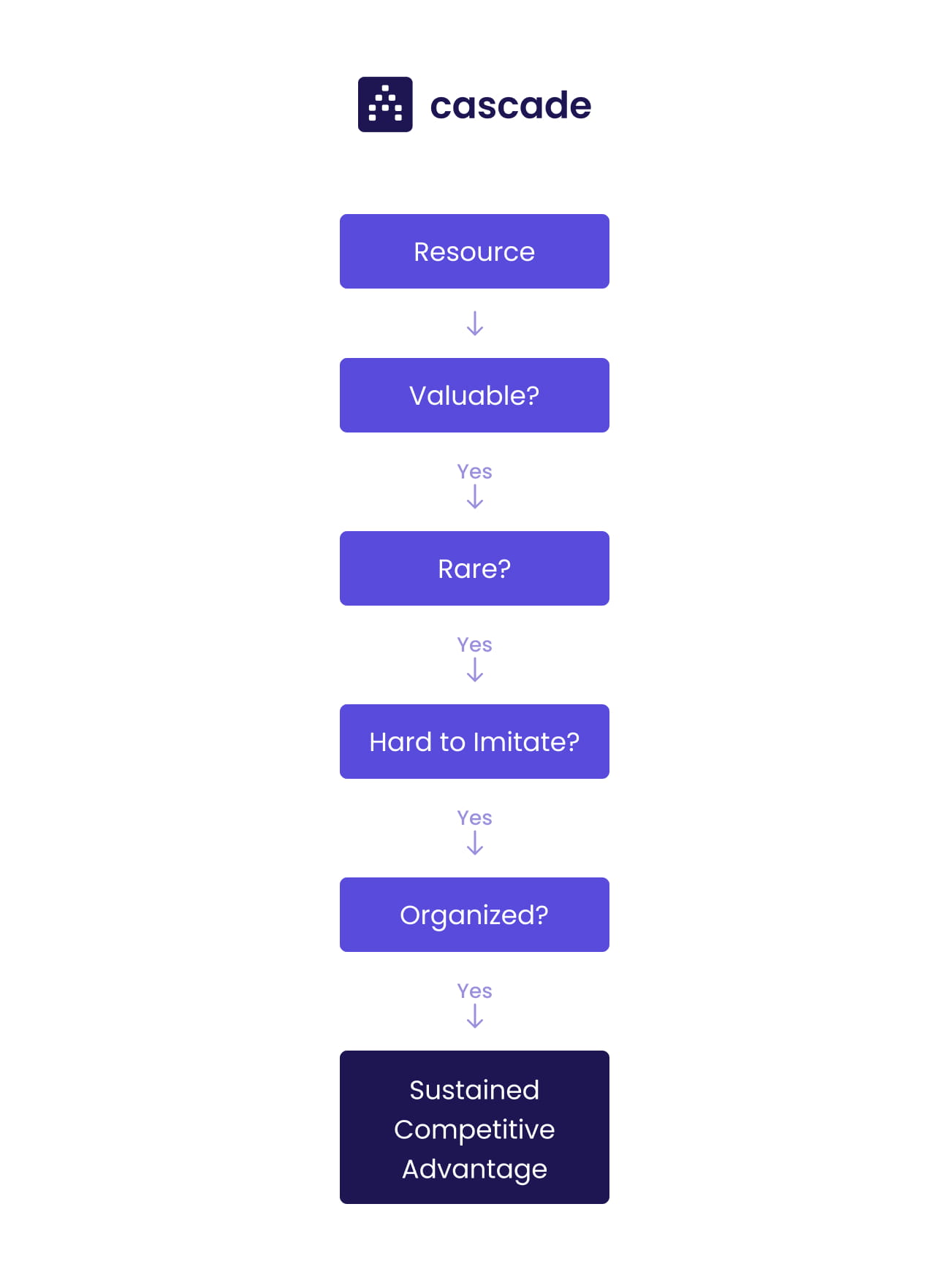
The acronym VRIO stands for value, rarity, imitability, and organization. This is the four-question framework used to evaluate the resources and capabilities of an organization. Now, what is a VRIO Analysis?
What Is A VRIO Analysis?
VRIO Analysis is an internal analysis tool used by organizations to categorize their internal resources based on whether they hold certain traits outlined in the framework. This categorization then allows organizations to identify the company resources that provide a competitive advantage. The VRIO Analysis is an Internal Analysis tool.
The VRIO Model:
- Valuable
- Rare
- Inimitable
- Organized
We'll go into more detail about each of the dimensions in a moment. First, we would like to explain why the VRIO analysis is such a popular tool. Jay Barney conceived the VRIO analysis in 1991.
Though we should mention, Barney originally conceptualized the framework as VRIN, the last dimension in the framework was “Non-Substituable”. The framework was refined over the years, and the N in VRIN became an O.
The framework is simple to understand, easy to use, and can provide enormous value for organizations to achieve a resource-based view of their business with the objective of staying ahead of competitors. This has made the tool an obvious choice for many companies looking to analyze their internal environment.
The premise of identifying a firm's resource as a competitive advantage is whether it passes through the dimensions of the framework.
📚 Recommended read: “Firm Resources And Sustained Competitive Advantage”—Jay Barney, 1991.
💡Pro Tip: Just like the VRIO Analysis, there are countless strategy frameworks out there, and we've covered a few that we think are extremely flexible and battle-tested over the years. Check them out!
- SWOT Analysis Template: How to do vital strategy groundwork
- Unlocking the Power of the Balanced Scorecard
- Porter's Five Forces (2023): The Definitive Overview (+ Examples)
- Value Chain Analysis: Overview, How To Use It (With Examples)
- McKinsey's Three Horizons of Growth Can Help You to Innovate
- The Ansoff Matrix Helps Organizations To Grow
The VRIO Framework Explained
Valuable resources
When a resource is valuable, it provides the organization with some sort of benefit. However, a resource that is valuable and doesn't fit into any of the other dimensions of the framework, is not a competitive advantage. An organization can only achieve competitive parity with a resource that is valuable and neither rare nor hard to imitate.
To assess resource value, ask the following questions:
- Does it benefit our customers or our bottom line?
- Does it align with our business strategy and goals?
- Can it improve our competitive positioning?
Rare resources
A resource that is uncommon and not possessed by most organizations is rare. When a resource is both valuable and rare, you have a resource that gives you a competitive advantage.
The competitive advantage achieved from a resource that is both valuable and rare is usually short-lived, though. Competitors will quickly realize and can imitate the resource without too much trouble. Therefore, it's only a temporary competitive advantage.
Here are some questions to understand if your resource is “rare”:
- Is it unique in our industry?
- Do competitors lack it?
- Is it a source of competitive advantage?
Inimitable resources
Resources are hard to imitate if they are extremely expensive for another organization to acquire them. A resource may also be hard for an organization to imitate if it's protected by legal means, such as patents or trademarks.
Resources are considered a competitive advantage if they're valuable, rare, and hard to imitate. However, organizations that aren't organized to take advantage of the resource fully, may mean the resource is an unused competitive advantage.
To analyze “inimitability”, ask the following questions:
- Is it hard for competitors to copy?
- Are there barriers to imitation? If yes, what are they?
- Does it require specialized knowledge or technology?
Organized resources to capture value
An organization's resource is organized to capture value only if it is supported by the processes, structure, and culture of the company. A resource that is valuable, rare, hard to imitate, and organized to capture value is a long-term competitive advantage.
💡Pro Tip: A resource cannot confer any advantage for a company if it’s not organized to capture the value.
Only a firm that is capable of exploiting valuable, rare, and imitable resources can achieve sustained competitive advantage.
Finally, these questions will help you understand if the resource is organized:
- Do we have the processes to use it effectively?
- Is there a clear strategy for its use?
- Are there mechanisms for continuous improvement?
VRIO Analysis Pros & Cons
Like any analytical framework, VRIO comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let's dive into them to understand when it's a strategic asset and when it might need support from other approaches.
✅ Pros
- Core strengths: VRIO helps identify core competencies, which can be crucial for creating a sustainable competitive advantage.
- Strategic guidance: Offers a structured approach to strategic decision-making by evaluating internal resources and capabilities in relation to competitive advantage.
- Competitive insights: Enables organizations to gain insight into why some resources or capabilities outshine their competitors.
- Resource efficiency: Aids in efficient resource allocation by directing investment toward resources and capabilities that are valuable, rare, and difficult to imitate.
- Competitive position: Enhances understanding of an organization's current competitive positioning and the potential for improving it.
❌ Cons
- Simplicity: Can oversimplify complex decision-making by focusing primarily on internal factors while ignoring external market dynamics.
- Subjectivity: The assessment of criteria like "Value" and "Inimitability" can be subjective and may vary depending on who is conducting the analysis.
- Static view: Offers a snapshot of an organization's resources and capabilities at a given point in time, missing dynamic market changes.
- Limited focus: Doesn't consider external factors, such as market trends, customer preferences, or regulatory changes, which can significantly impact an organization's strategy.
- Resource-intensive: Conducting a thorough VRIO analysis can be resource-intensive and time-consuming, which may be impractical in fast-paced business environments.
💡Pro Tip: VRIO analysis provides valuable insights into internal strengths and weaknesses, but it should be part of a broader strategic toolkit to ensure a comprehensive approach.
VRIO Analysis Example
To use the framework, you'll need first to define your resources. Your organization will surely have both tangible and intangible resources, which generally fall into one of the following categories:
- Financial resources such as money, shares, bonds, and debentures.
- Human resources such as the skills of your people and the knowledge of your people.
- Material resources such as raw materials, facilities, machinery, and equipment.
- Non-material resources such as patents, brand names, and intellectual property.

Once you've defined all your resources, take each resource through the VRIO framework and categorize each based on the traits it holds. Categorize resources into one of the following groups: competitive parity, temporary competitive advantage, unused competitive advantage, or long-term competitive advantage.
The framework below should help you visualize the process.
.jpeg)
Once you've categorized your resources into the four categories, you should have a good understanding of where your competitive advantages lie and whether they'll be short or long-term advantages.
VRIO Resources
With your resources categorized through the VRIO framework, you can now start to analyze each.
- Are there any competitive implications?
- Is there a potential for improvement in certain resources?
The aim is to find the resources that have the potential to move from their current category into a higher one. For example, an organization may have a resource that is valuable and rare, such as a certain invention they created.
They deem their invention a temporary competitive advantage as per the VRIO analysis. The organization comes to this conclusion because they decide it wouldn't be difficult or expensive for a competitor to imitate the invention if they wanted to.
Upon analysis, the organization sees an opportunity to move its temporary competitive advantage to a higher category.
After some analysis, they discover that if they can obtain a patent for their invention, the resource would then become very difficult for competitors to imitate. The resource would then enter a higher category, as it is valuable, rare, and hard to imitate.
The process of analyzing your internal environment is extremely important in the strategic planning process. While this article has only focused on the VRIO framework, there are many other internal analysis tools that can be used by organizations to assist them with strategic planning.
We should also mention that an external analysis that provides a comprehensive understanding of external factors (such as the PESTLE Analysis) is just as crucial in the strategic planning process.
VRIO Analysis For A Sustainable Competitive Advantage
As previously mentioned, a resource that is a competitive advantage is not a guarantee of value provided to the organization. The resource may be unused by the organization, or it may be only a temporary advantage, which could eventually become a competitive disadvantage if rivals catch up.
What organizations really need to create is a sustainable competitive advantage. However, creating this is much easier said than done.
👉🏻 So now that we've categorized your resources and analyzed those with potential, where to next?
The category that usually poses the biggest potential for improvement is the unused competitive advantage category.
These resources are already competitive advantages, they only lack the organization required to fully utilize them and gain value from them. This is where your strategic plan comes into play.
Developing a strategic plan that takes these unused competitive advantages into account and works to support these resources through strategic management will allow companies to transform their resources into sustained competitive advantages.
A strategic plan will align the processes, people, and structure needed to support these resources and turn them into sustainable competitive advantages.
By no means is this an easy or quick solution. Developing a good strategic plan that exploits your unused competitive advantages is only the beginning. You need to implement it, set clear metrics, and constantly monitor the progress of the strategy to ensure its successful execution.
Luckily, we've already created articles that will help you on your next part of the journey, creating your strategic plan: How to Write a Strategic Plan That Gets Results + Examples.
Free VRIO Analysis Template
Hopefully, this article has given you a better understanding of the value the VRIO Framework can bring to organizations. If you're interested in better identifying your organization's competitive advantage, make sure to try our Free VRIO Analysis Template!
FAQs
What’s the difference between VRIO and SWOT Analysis?
VRIO Analysis and SWOT Analysis are strategic tools used by organizations, but they have different focuses and purposes:
- VRIO focuses on evaluating internal resources and capabilities to determine sustainable competitive advantages through four criteria: Value, Rarity, Inimitability, and Organization.
- In contrast, SWOT Analysis provides a broader view by assessing an organization's Strengths and Weaknesses (internal factors) along with Opportunities and Threats (external factors).
While VRIO is more strategic and forward-looking, SWOT offers a comprehensive perspective, considering both internal and external factors.